Addison's disease |
Basic Information
What is Addison's disease?
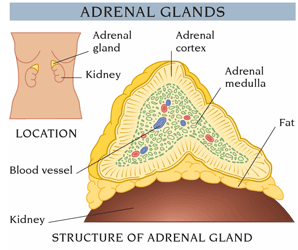
Gradual, progressive destruction of the adrenal glands, which are located over the kidneys. The adrenal glands secrete several hormones that are essential to a number of body functions. These hormones help to maintain body fluid balance and are involved in sugar and protein metabolism, maintenance of blood pressure, and response to physical stress. Addison's is rare, but can occur in all age groups and about equally in men and women. Symptoms may develop slowly over months or years.
Frequent signs and symptoms
- Weakness and fatigue.
- Gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and appetite and weight loss).
- Low blood pressure causing faintness and dizziness.
- Brownish skin (looks suntanned) with white patches.
- Darkening of freckles, scars and nipples.
- Hair loss.
- Feeling cold all the time.
- Dramatic behavior or mood changes, including aggression or depression.
Causes
- Symptoms and signs are caused by low levels of cortisone- like hormones produced by the adrenal glands. The cause of adrenal insufficiency is usually unknown, but is believed to be an autoimmune disorder.
- It also may be a consequence of the following disorders: tuberculosis, cancer, pituitary disease, AIDS.
- Use of oral cortisone drugs for other conditions. When cortisone is withdrawn, normal adrenal function sometimes does not return.
Risk increases with
Stress, diabetes mellitus, surgery, anticoagulant therapy.
Preventive measures
Don't discontinue use of cortisone drugs or change the dosage without medical advice.
Expected outcomes
- If diagnosed in early stages, the symptoms can be controlled with hormone-replacement treatment, and a normal lifestyle can be maintained.
- In advanced stage, this disorder is fatal without treatment.
Possible complications
- Adrenal crisis (pains, weakness, low blood pressure, high or low temperature, fainting) caused by injury or illness.
- Misdiagnosis as a mental condition.
- Increased susceptibility to infections.
Addison's Disease Treatment
General measures
- Diagnostic tests may include laboratory blood studies and the metyrapone test to measure adrenal function.
- This is a life-long condition. Learn how to care for yourself. Strict attention to medication schedules is vital.
- Learn about adrenal crisis and its relationship to body stress (infection, surgery or injury).
- Advise any doctor and dentist who treats you that you have Addison's disease.
- If you live or travel where medical care is not readily available, you should be given instructions on giving yourself cortisone injections in case of emergency.
- Wear a medical alert type bracelet or pendant to indicate you have Addison's disease and the name of the drug and dosage that you take.
- Stay up-to-date on immunizations, including those for influenza and pneumonia.
- Hospitalization for an adrenal crisis.
- Further information is available from the National Addison's Disease Foundation
Addison's disease Medication
You will be prescribed one of several types of cortisone drugs. A mineralocortoid often is needed to help control salt and mineral balance. Follow medication schedule exactly. Never change or omit medication without doctor's advice.
| Information | Brand | Generic | Label | Rating |
 |
Deltasone | Prednisone | ||
| Decadron | Dexamethasone | |||
| Florinef | Fludrocortisone |
Activity
No restrictions.
Diet
Special diet may be necessary (e.g., one to maintain proper balance of sodium and potassium or to increase protein or carbohydrate intake).
Notify your physician if
- You or a family member has symptoms of Addison's disease, especially an adrenal crisis. Call immediately. Adrenal crisis is an emergency!
- The following occur after diagnosis:
- Any signs of infection, such as fever, chills, muscle aches, headache and dizziness.
- Serious injury, such as bone fracture, dislocation or internal injuries.
- You are scheduled for elective surgery or require anesthesia for any reason.
- New, unexplained symptoms develop. Drugs used in treatment may produce side effects, such as protruding abdomen, thin extremities, puffy face and eyes, acne and growth of facial hair.
Last updated 6 October 2015
