Iron deficiency anemia |
Basic Information
Description
A decreased number of circulating blood cells or insufficient hemoglobin in the cells. Anemia is a result of other disorders. For proper treatment, the cause must be found.
Signs and symptoms of Iron-deficiency anemia
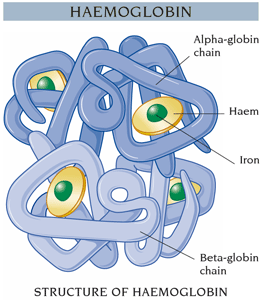 Initially there may be no symptoms.
Initially there may be no symptoms.
Signs of pronounced anemia include:
- Tiredness and weakness.
- Paleness, especially in the hands and lining of the lower eyelids.
Less common signs include:
- Tongue inflammation.
- Fainting.
- Breathlessness.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Appetite loss.
- Abdominal discomfort.
- Cravings for ice, paint or dirt.
- Susceptibility to infection.
Causes
Decreased absorption of iron or increased need for iron. Causes in adolescents and adults:
- Rapid growth spurts.
- Heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Pregnancy.
- Malabsorption.
- Gastrointestinal disease with bleeding, including cancer.
Risk increases with
- Poor nutrition.
- Age over 60.
- Recent illness, such as an ulcer, diverticulitis, colitis, hemorrhoids or gastrointestinal tumors.
Preventive measures
- Maintain an adequate iron intake through a well-balanced diet or iron supplements.
- Correction of gynecologic or other problems causing excess blood loss.
Expected outcomes
Usually curable with iron supplements if the underlying cause can be identified and cured.
Possible complications
- Failure to diagnose a bleeding malignancy.
- Angina pectoris (pain or pressure beneath the breastbone caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart) or congestive heart failure (pumping action of the heart is insufficient) may develop as a result of marked iron deficiency.
Iron deficiency anemia treatment
General measures
- The most important part of treatment for iron-deficiency anemia is to correct the underlying cause. Iron deficiency can be treated well with iron supplements.
- Avoid risk of infections.
Medications
Iron supplements:
- Take iron on an empty stomach (at least 1/2 hour before meals) for best absorption. If it upsets your stomach, you may take it with a small amount of food (except milk).
- If you take other medications, wait at least 2 hours after taking iron before taking them. Antacids and tetracyclines especially interfere with iron absorption.
- Iron supplements may cause black bowel movements, diarrhea or constipation.
- Continue iron supplements until 2 to 3 months after blood tests return to normal.
- Too much iron is dangerous. A bottle of iron tablets can poison a child. Keep iron supplements out of the reach of children.
Activity
No restrictions. You may need to pace activities until symptoms of fatigue are gone.
Diet
- Adults should limit milk to 1 pint a day. It interferes with iron absorption.
- Eat iron-containing foods, including meat, beans and leafy green vegetables.
- Increase dietary fiber to prevent constipation.
Notify your physician if
- You or a family member has symptoms of anemia.
- Nausea, vomiting, fever, stomach pain, severe diarrhea or constipation occur during treatment.
Last updated 14 June 2015
